Federal IT spending remained robust throughout FFY24, and the market appears poised for another strong year in FFY25, even as CY25 begins with yet another continuing resolution
TBR projects weighted average year-to-year federal IT services revenue growth for the 11 companies featured in our Federal IT Services Benchmark will decelerate to between 8% and 8.5% in 4Q24, down from 9.3% in 3Q24. Additionally, we anticipate weighted average year-to-year revenue growth in the defense sector will fall to between 6.8% and 7.3% in 4Q24, while civilian revenue growth will remain between 10% and 10.5% in 4Q24.
Four leading federal systems integrators — Booz Allen Hamilton (BAH), CACI, Leidos and SAIC — as well as smaller federal IT peer KBRWyle elevated their respective revenue growth forecasts for their current fiscal year when tendering 3Q24 fiscal results; these results indicate the federal IT macro environment will remain mostly growth-friendly through FFY25.
The new federal fiscal year began with a continuing resolution (CR) that extended government funding until Dec. 20, when a subsequent CR was enacted to fund federal operations until March 14, 2025. Further CR extensions in federal fiscal year 2025 (FFY2025) would cause budget delays that could impede the ability of federal IT contractors to convert backlog into revenue, but most vendors expect revenue growth to remain on a solidly upward growth trajectory in FFY25.
The Fiscal Responsibility Act of 2023 (FRA) remains in effect, and the Biden administration’s FFY25 budget request aligns with the FRA’s spending caps. Federal IT spending priorities will remain largely unchanged in FFY25, with IT investment focused on enhancing national security (especially in the APAC region and to deter future Russian aggression in Ukraine), promoting the adoption of AI and generative AI (GenAI) technologies, modernizing and enhancing the security of federal technology infrastructures, and IT-enabling public health systems.
The Department of Defense (DOD) will be integrating six new naval vessels into its global IT networks while spending nearly $34 billion to enhance space-based capabilities and another $10 billion to enhance the security and interoperability of IT and weapons systems operating in the Indo-Pacific theater. The Pentagon will spend another $14.5 billion for overall cybersecurity activities in FFY25 while expanding outlays on analytics and AI and increasing investment in the ongoing Replicator initiative to deploy thousands of autonomous systems across multiple domains by FFY26 to counter the ever-growing threat from China.
Civilian agencies will continue increasing their cybersecurity spending in FFY25, with an additional $13 billion requested in FFY25 to fund new zero-trust and access management programs as well as initiatives to secure critical infrastructure and federal civilian supply chains. The budget of the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA), the division of the Department of Homeland Security (DHS) charged with leading cybersecurity efforts across the federal market, will expand by over $100 million from FFY24 to FFY25 to reach $3 billion. Civilian agencies are also increasing AI-related investments to fund the development, testing, purchase and deployment of new AI and GenAI technologies, as well as to expand their AI workforces.
Expansion accelerated in the federal IT market in 3Q24 as renewed M&A activity by several federal IT vendors augmented strong, stable demand for digitally based IT modernization
Statutory year-to-year revenue growth for the 11 TBR-benchmarked vendors in the U.S. federal market on a weighted average basis rose 100 basis points sequentially, increasing from 8.3% in 2Q24 to 9.3% in 3Q24. Acquisitions by Accenture Federal Services (Cognosante), BAH (PAR Government Systems Corporation [PGSC]), CACI (Quadrint in 1Q24 and Azure Summit Technologies [AST] in 3Q24), CGI Federal (Aeyon), General Dynamics Technologies (Iron EagleX) and KBRWyle (LinQuest) generated an inorganic tailwind to overall market growth of roughly 180 basis points in 3Q24.
Federal IT executives (e.g., CACI CEO John Mengucci) have indicated that the M&A market became more buyer-friendly during 2024, prompting several benchmarked vendors to leverage acquisitions to address portfolio gaps in multiple areas, including digital transformation (DT) and emerging technologies for classified defense and intelligence operations.
Vendors have been acquiring, and will continue to hunt for, smaller peers with scalable cloud and digital modernization capabilities as well as deep existing (and likely cloud-related) relationships with federal agencies. Underpinning inorganic market growth is enduring robust demand for digitally transformative technologies in AI, cloud, analytics and data science, as well as the continued need to upgrade baseline IT infrastructures across the federal sector to accommodate digital modernization.
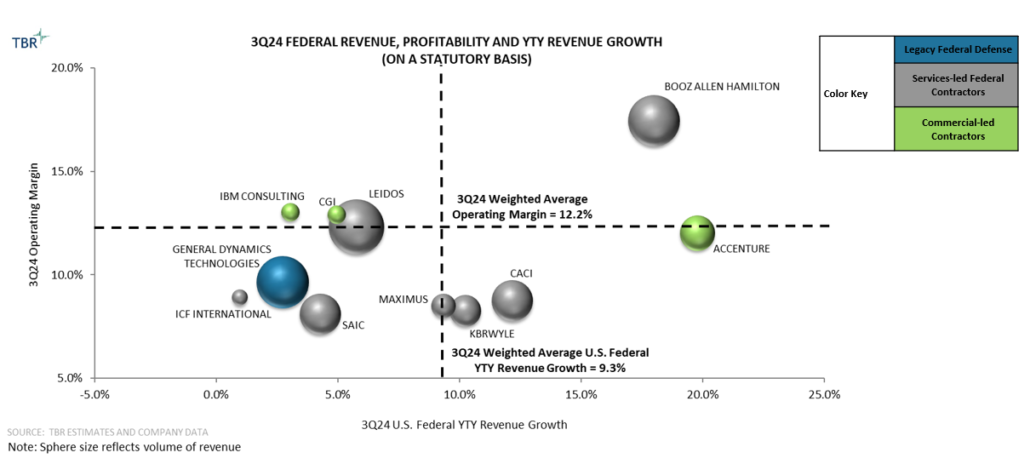
KBRWyle’s federal revenue rose 10.2% year-to-year in 3Q24 as LinQuest was acquired and demand mounted for all the offerings within Government Solutions business units. KBR’s leadership team increased its guidance for the company’s revenue, adjusted EBITDA and adjusted earnings per share (EPS) during the 3Q24 earnings call due in part to Government Solutions’ strong performance and the purchase of LinQuest creating more opportunities with DOD agencies.
Inorganic growth is again boosting CACI’s top-line growth after the company made three acquisitions between 2Q24 and early 4Q24. CACI’s acquisition of AST in 3Q24 contributed between 70 and 80 basis points of inorganic growth during the quarter and is expected to add between $440 million and $450 million to the company’s sales in its FY25.
BAH’s revenue rose 18% year-to-year in 3Q24, driving the firm’s total sales past $3 billion for the first time. BAH’s June acquisition of PGSC began to contribute inorganic revenue in 3Q24, and we estimate BAH’s organic year-to-year growth was 17.7% in 3Q24, with PGSC contributing between 20 and 30 basis points of inorganic growth.
Civil and defense agencies drive double-digit IT growth through cybersecurity, health IT and AI investments
Civil agencies continue to aggressively invest in cybersecurity, health IT and Agile-based software systems, leading to sustained double-digit civil sector IT spending growth
Weighted average growth in the civilian sector accelerated 80 basis points sequentially, rising from 9.6% in 2Q24 to 10.4% in 3Q24. Vendors including BAH and Leidos have posted multiple quarters of double-digit growth in their respective civil units as of 3Q24, with robust rates of growth expected to persist well into 2025. Sector growth was sustained at or near 10% throughout FFY24 as demand among civil agencies remains robust for comprehensive zero-trust and cyber incident support solutions, particularly by DHS, the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS), the IRS and NASA.
Attracting and retaining cybersecurity talent also remain top priorities for nearly all civilian agencies, which are tapping vendors like Accenture Federal Services (AFS), BAH and Deloitte Federal for human resource advisory services. NASA launched an eight-year, $2 billion program, NASA Consolidated Applications and Platform Services (NCAPS), during 3Q24 to develop and deploy Agile-based software for over 200 IT systems, with vendors including CACI among the primary awardees. Health IT is generating new revenue and profit streams for the benchmarked vendors, and agencies including the HHS (and its subagencies, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services, the Center for Disease Control and Prevention, and the National Institutes of Health) are seeking agencywide AI and analytics adoption services. The top five benchmarked vendors in year-to-year civilian sector revenue growth in 3Q24 were AFS (25%), BAH (16.1%), SAIC (10.8%), Maximus (9.3%) and CACI (7.9%).
Defense and intelligence agencies expanded spending on IT modernization, global integration of defense networks, and AI-enabling intelligence collection and analysis solutions in 3Q24
Weighted average expansion in the defense sector rose 110 basis points sequentially, from 7.5% in 2Q24 to 8.6% in 3Q24. BAH and CACI maintained double-digit expansion in their respective defense sales in 3Q24, while Leidos and GDT posted midsingle-digit top-line defense growth in the quarter. The DOD awarded billions of dollars in net-new programs while several benchmarked competitors also secured key recompetes with defense agencies. The DOD’s European Command has aggressively expanded its activities (particularly with BAH) as the war in Ukraine grinds on, while globally, the Pentagon continues prioritizing the adoption of AI, analytics, big data and cloud technologies to facilitate and accelerate real-time decision making for military commands.
The DOD is also expanding activities in APAC, investing in advanced intelligence and combat-related technologies to deter Chinese aggression. The U.S. Air Force is accelerating spend on the Collaborative Combat Aircraft program while the DOD’s Combined Joint All Domain Command and Control (CJADC2) initiative to achieve IT infrastructure interoperability across all military branches and with defense agencies of U.S. allies continues to spool up. Project volumes also expanded on several marquee defense IT programs, including Sentinel (modernizing C5ISR [Command, Control, Communications, Computers, Cyber, Intelligence, Surveillance and Reconnaissance] systems across the DOD) and the $11 billion Defense Enclave Services program.
IT investment patterns in the intelligence community continue slowly stabilizing as intelligence agencies invest in intelligence analysis services and solutions and AI-based technologies to collate and ingest intelligence data. The top five benchmarked vendors in year-to-year defense sector revenue growth in 3Q24 were BAH (19.1%), CACI (13.5%), KBRWyle (12.4%), Leidos (4.4%) and AFS (3.9%).
Follow federal IT services performance throughout 2025 with data and analysis in TBR Insight Center. Start your free trial today.