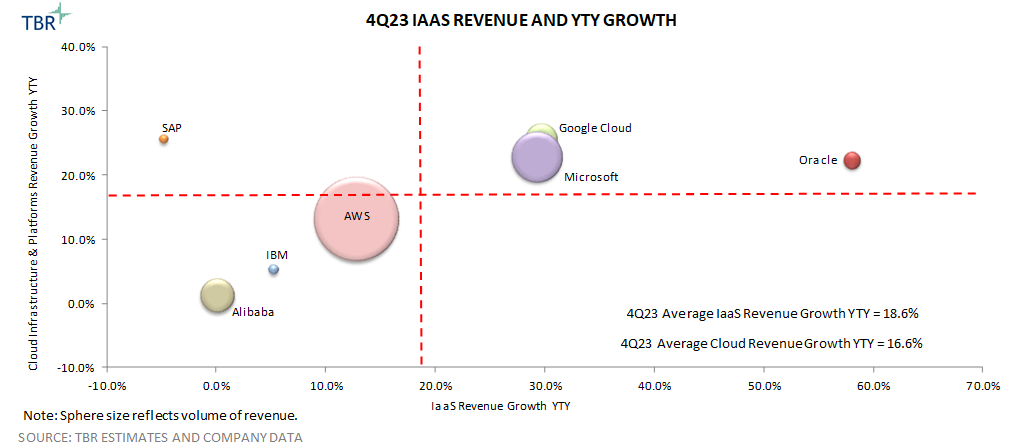
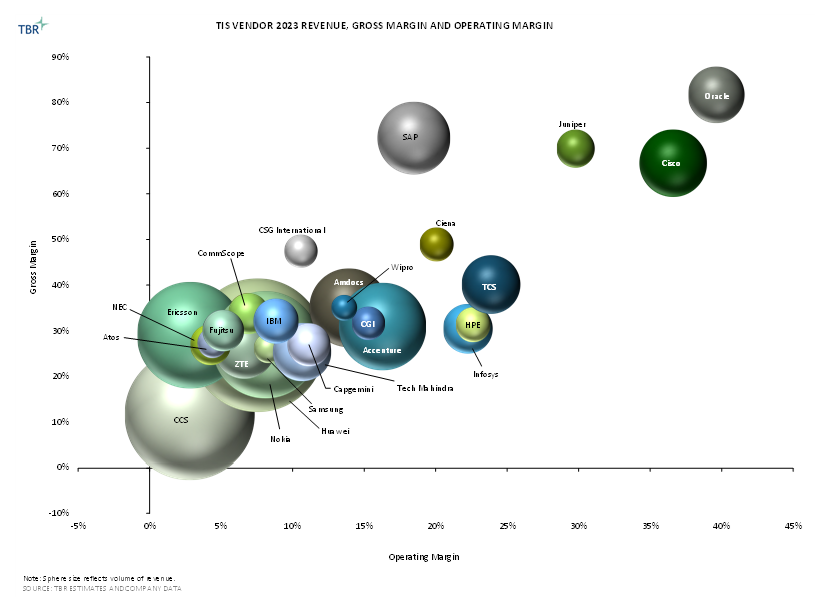
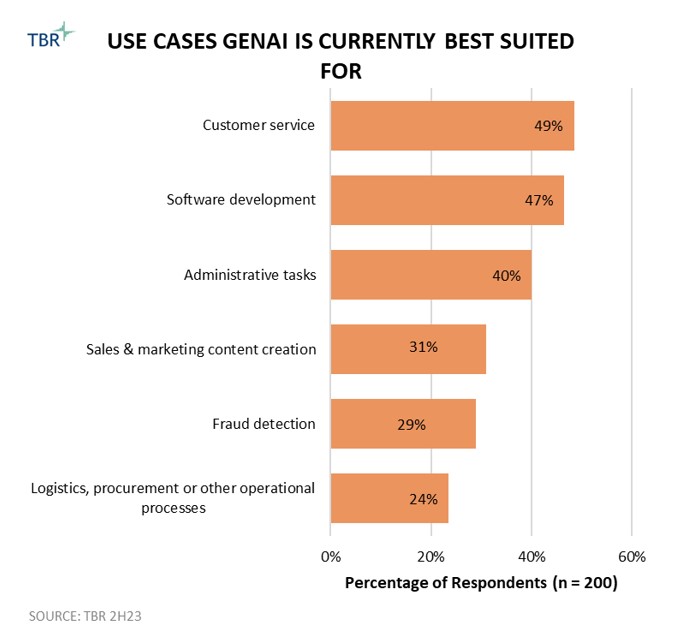
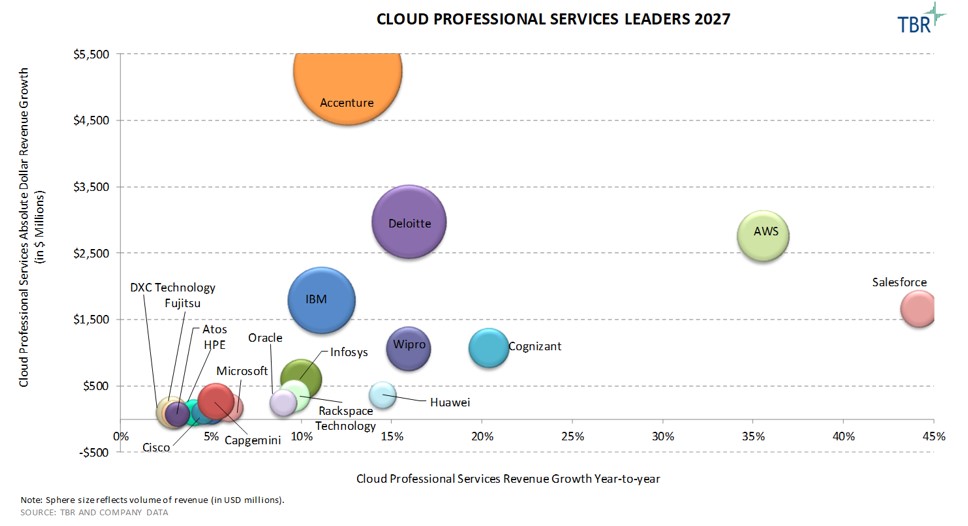
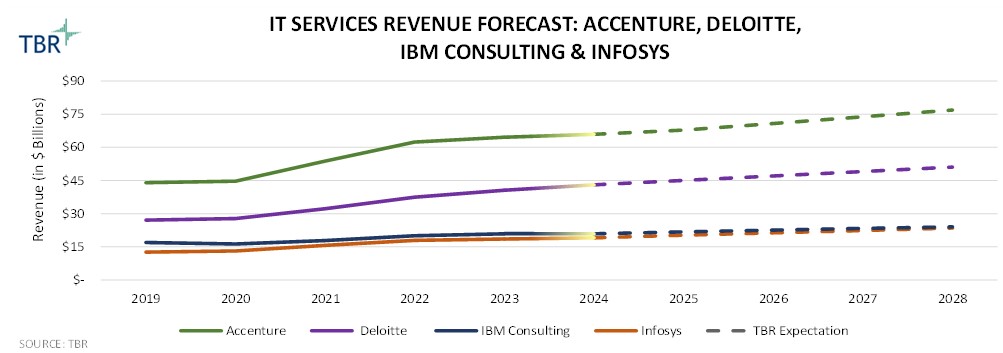
Overall Revenue and Trends
In late 2023 and thus far in 2024, the companies within TBR’s IT Services coverage faced pressures within their respective financial services practices, experiencing industry declines from a revenue perspective as higher interest rates limited opportunities and hindered growth trajectories.
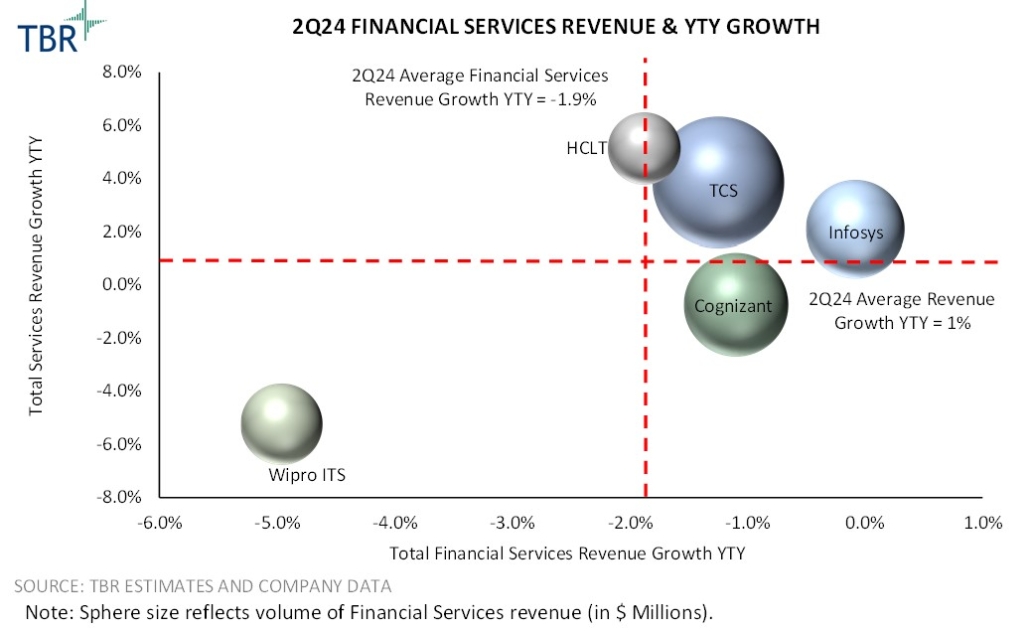
The India-centric vendors TBR covers — Cognizant, HCLTech, Infosys, Tata Consultancy Services (TCS) and Wipro IT Services (ITS) — experienced these financial services revenue declines, despite their efforts to embed automation, AI and efficiency-driven services.
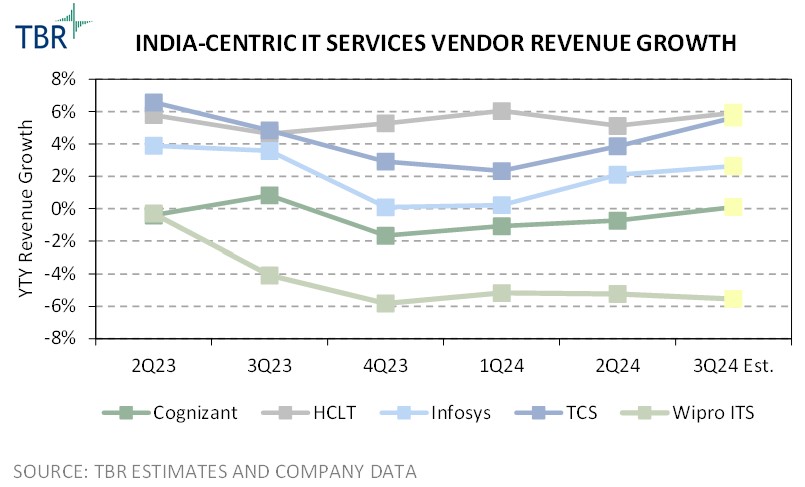
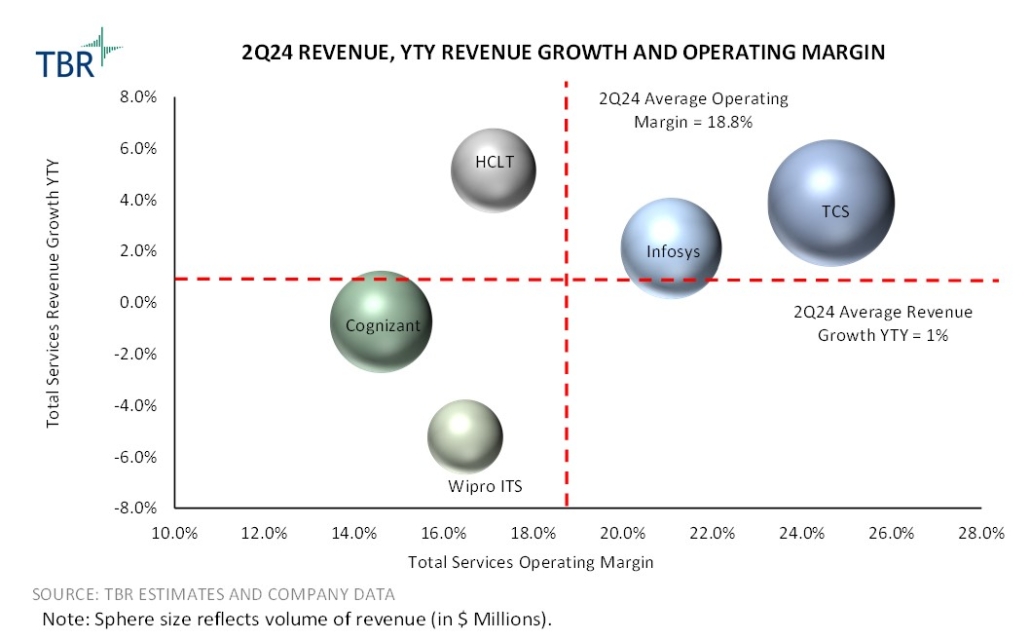
The five vendors experienced mixed performance in terms of overall revenue in 2Q24 and pursued varying portfolio expansions and strategy directions. Growth leaders HCLTech, Infosys and TCS have benefited from demand for cloud migration, application management and digital services, which helped to offset declines in financial services revenue. Digital services enabled by innovation-led frameworks remain an important sales engine for Infosys, helping the company build a foundation for future performance.
While HCLTech also leverages Digital Workplace Services, the company’s engineering expertise provides an avenue of differentiation as well as relationship building through developed infrastructure and solutions. HCLTech’s integration of its Engineering and R&D Services sales with its IT and Business Services practice enables the company to better address demand for transformation services that stretch across multiple segment groups, driving value creation.
Meanwhile, demand for next-generation solutions across connected plants, connected services and intelligent product engineering is boosting TCS’ Digital Transformation Services revenue.
Revenue growth for both Cognizant and Wipro ITS was more sluggish during 2Q24 as the companies struggled to capture new opportunities amid limited discretionary spend. Cognizant is experiencing longer contract periods from larger engagements, which extends the revenue generation but leads to smaller pockets of revenue recognition. Wipro is in a slightly more precarious position as it appoints new leadership and establishes new strategic directions. While the investments and leadership transitions will help Wipro evolve its portfolio, the company will continue to struggle to accelerate revenue growth and expand market presence.
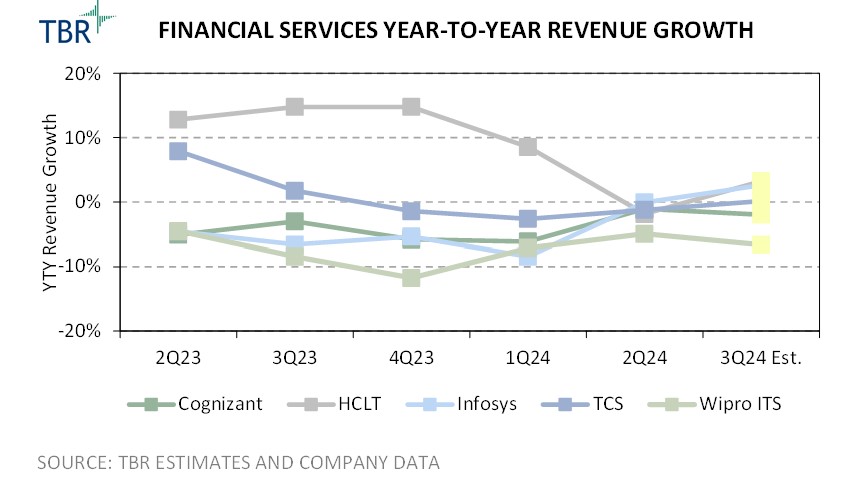
Financial Services
For the India-centric IT services vendors, financial services revenue performance has been hit harder relative to overall revenue as the macro environment remains challenged. Inflation rates, higher interest rates and ongoing economic uncertainty have pushed financial services companies, primarily within the banking space, to reduce budgets and prioritize cost cutting. While financial services companies look to invest in data, AI, cloud and digital platforms, spending restrictions have led to a focus on cost optimization through cloud and digital services.
Wipro experienced the greatest impacts on its financial services revenue, owing largely to overall market pressures. The company continues to struggle to fully capitalize on existing client relationships and create upselling opportunities. Leveraging its AI solutions and services for modernization could support the company’s efforts to forge additional discussions among insurance clients but will not offset limited interactions within the banking space. Wipro will likely prioritize engaging with insurance clients rather than banking institutions to generate revenue streams during 2024.
Infosys followed Wipro in terms of financial services performance, as a contract renegotiation within the financial services vertical reduced revenue growth by 100 basis points, which negatively impacted Infosys’ P&L and pressured margins. However, there are signs of improvement for Infosys in the segment, with increased activities in the U.S. and six large financial services deals signed in 1Q24. The deals likely comprise a mix of both insurance and banking clients. High inflation and interest rates are limiting client spend, pushing more vendors to prioritize workload and operations optimization.
Cognizant also experienced the impacts of limited budgets among its financial services clients. As conditions begin to improve, however, Cognizant management has highlighted new activities around personalization services as well as infrastructure and platform modernization, bringing in opportunities in the industry. Cognizant aims to grow its industry knowledge and specific offerings to better engage with clients and deliver personalized solutions. To address demand, Cognizant will look to create customer experience solutions and workload optimization offerings that leverage AI to strengthen its connection with clients in the sector.
TCS leverages the TCS BaNCS platform to deliver digital transformation services to a variety of financial services clients using a SaaS model or through the cloud. The platform supports infrastructure, application and workflow transformation, enabling users to modernize their environments, enhance customer engagement, utilize data and analytics, and accelerate innovation efforts. The platform allows TCS to deliver core banking transformations for clients and provides more personalized financial management services that can be aligned with budgets.
With demand around cloud and AI transformation projected to increase, TCS will develop new capabilities and functions such as TCS BaNCS for Intelligent Experience, allowing for the utilization of data and AI services across banking environments.
HCLTech offset a good amount of financial services pressures, benefiting from its digital marketing, data management, digital workplace services and IT transformation. The company was better able to withstand macroeconomic impacts, owing to its software application portfolio as well as experience around data services. Further, the company’s client management strategy enables HCLTech to solidify client relationships, allowing it to capture smaller-scale budget-friendly projects that are geared toward improving business operations and client interactions.
Conclusion
Vendors have taken different approaches to capitalize on financial services opportunities as macroeconomic challenges ease. One approach is to focus on the insurance sector, which was more protected from the impacts of reduced customer budgets than the banking sector.
While HCLTech maintained a steady performance, generating growth in financial services when excluding 2Q24, its peers invested in portfolio offerings that aligned with trends and demand for data, customer experience, cloud migration and IT modernization. During the remainder of 2024 and into 2025, HCLTech and TCS will likely be stronger candidates for financial services engagements, leveraging large platforms and solutions such as the TCS BaNCS platform to lead the technology-driven transformation across the industry.
Further, Infosys could pressure its India-centric peers, leaning on recent investments to strengthen its professional services positioning, such as through the acquisition of in-tech, which bolstered the company’s engineering services.
TBR publishes quarterly assessments of these IT services companies as well as others in the IT services, cloud, software, consulting, telecom, infrastructure and devices spaces. To access all current and historical data and analysis, start your TBR Insight Center™ free trial today.