KPMG Shifts Focus to Legal Services and AI-driven Strategy Consulting
KPMG is leaning toward legal services and AI-infused strategy consulting offerings to bolster sales as the firm navigates choppy market conditions within core deal advisory
Earlier in January news reports surfaced that a subsidiary of KPMG, KPMG Law US, had applied to operate in Arizona under a state program allowing nonlawyers to operate law firms and provide legal services in the state. This aligns with our Fall 2024 Management Consulting Benchmark Vendor Profile: KPMG, in which we discussed this topic.
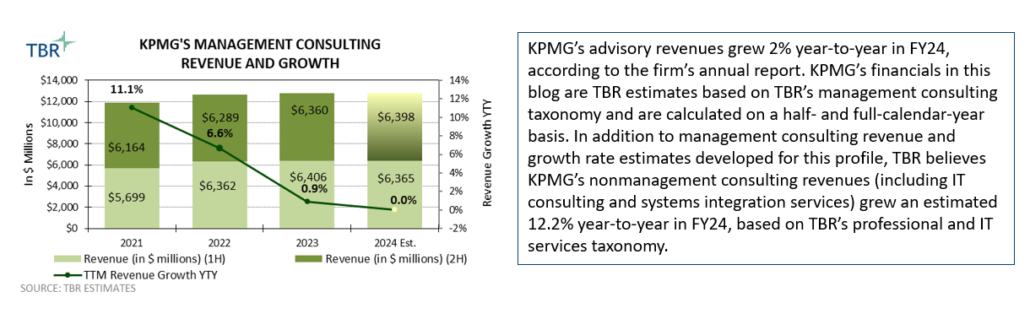
KPMG’s revenue growth decelerated from 0.7% year-to-year in 1H23 to -0.6% year-to-year in 1H24 as the firm continued to face pressure in core markets such as deal advisory despite the uptick in signings — a trend we expect to continue into 2025 as we estimate management consulting sales to stay flat on an annual basis. Over the last six months, KPMG signed M&A advisory and restructuring deals, including those with Germany-based air-taxi manufacturer Lilium; Spain-based Santander Consumer Finance; and Romania-based retailer La Cocos. As KPMG seeks to diversify its portfolio and revenue opportunities, recent investments across its portfolio related to legal services suggest that demand across regions is choppy and that KPMG will be reviewing its positioning, one member firm at a time.
For example, in Australia, KPMG restructured its stand-alone legal services practice, folding KPMG Law’s Tax Controversy & Disputes practice under KPMG’s tax business. At the same time, in the U.S. KPMG is looking to invest heavily in AI to bolster its legal services offerings, creating a conduit for consulting business. Meanwhile, KPMG partnered with ContractPodAI to bolster its legal AI and contract lifecycle management capabilities as the firm seeks to expand its legal managed services opportunities targeting clients in the U.S., U.K. and Germany. We believe KPMG’s push in the legal services space can also help the firm gain access to the talent needed to enhance its governance, risk and compliance (GRC) value proposition, especially as more general counsels are getting involved in GenAI solution development.
Outside legal services and M&A advisory, we expect KPMG’s efforts to bolster its management consulting revenues will come from its investments in technology-centric capabilities, with AI and GenAI among the predominant topics impacting the firm’s strategy consulting sales. We believe the KPMG Lighthouse team will continue to provide a critical link enabling the firm to elevate conversations beyond the typical art-of-the-possible discussions and tying them to business outcomes with tangible solutions. While embedding AI and data science is not unique to KPMG, the firm has an opportunity to elevate the value of such offerings as the single most important technology the firm stands behind, especially as many of its competitors stretch their portfolios and messaging across multiple domains. While we understand this can be a tricky message to execute against, demonstrating depth and specialization will likely trump generalization moving forward as GenAI levels the knowledge field, helping KPMG stand out.
Legal services would only be part of KPMG’s story going forward, as we also discussed in the Fall 2024 Management Consulting Benchmark Vendor Profile: KPMG.
GenAI can help KPMG enhance its industry consulting expertise, provided the firm leans on partners to do the tech part and focuses on its business pain points
Healthcare was KPMG’s fastest-growing industry vertical at 6.4% year-to-year in 1H24, according to TBR estimates. As an outlier for KPMG’s growth, the vertical benefited from industry clients seeking to digitize health systems and improve the patient experience. KPMG is not alone in capturing high-growth opportunities in the healthcare sector as rivals Deloitte and Accenture have also captured robust sales expansions in the industry with both competitors enhancing value propositions through acquisitions including Gryphonic Scientific (biosafety and biosecurity) and Cognosante (federal health).
To counter competitive threats, KPMG leaned on organic means, announcing the opening of a Global Center of Excellence for healthcare based in Bermuda. While the center will bring in professionals from the Caribbean, Bermuda, the Crown Dependencies, and Mediterranean islands, it will also have access to KPMG’s broader network of 5,000 professionals across the firm’s service lines within the healthcare vertical, including 200 clinicians.
Outside healthcare, KPMG continued to rely on its industry consulting know-how to enhance portfolio capabilities around partner-enabled industry accelerators such as with Workday for Retail and Hospitality; with Meta using Meta’s open-source large language model (LLM) Llama to build solutions for internal audit and commercial loan processing, paving the way for opportunities within the financial services vertical; and with Salesforce around the use of Customer 360 solutions for healthcare, among other verticals.
TBR views these as important steps that are enabling KPMG to better compete with Big Four rival Deloitte, which has set its Industry Advantage program to drive long-term managed services and feed the Operate part of Deloitte’s business. In a recent conversation with KPMG’s Managed Services leadership, TBR got a chance to hear how KPMG is able to use the KPMG Powered part of its four-part framework — Connected, Powered, Trusted and Elevate — to drive conversations around industry pain points in verticals such as insurance and financial services that have helped generate managed services engagements. Additionally, leaning on strategic growth and delivery partners has helped KPMG demonstrate depth rather deviate from its core capabilities.
We expect KPMG’s next growth frontier to come from the firm’s ability to codevelop industry-specific small language models as clients look to take advantage of the power of GenAI without compromising security and privacy by using LLMs based on public data.