Cloud Voice of the Partner
TBR Spotlight Reports represent an excerpt of TBR’s full subscription research. Full reports and the complete data sets that underpin benchmarks, market forecasts and ecosystem reports are available as part of TBR’s subscription service. Click here to receive all new Spotlight Reports in your inbox.
Partners remain hopeful about GenAI opportunity but still need to build trust through monetization
Key takeaways
- Although generative AI (GenAI) is dominating partnership activities, the technology’s actual revenue contribution remains insignificant.
- Cloud providers have done a better job of reducing competition with partners, but it still happens, particularly at the field level.
- Everyone believes trust and transparency are key to a successful alliance, but cloud vendors place a lot of weight on more tangible factors, like pricing and coinvestment.
- When three parties are involved, win rate and deal size potential increase, but orchestrating these relationships remains a challenge, largely from a sales perspective.
Trust built on delivery, alignment and collaboration enables vendors and partners to present unified strategies and win complex enterprise deals
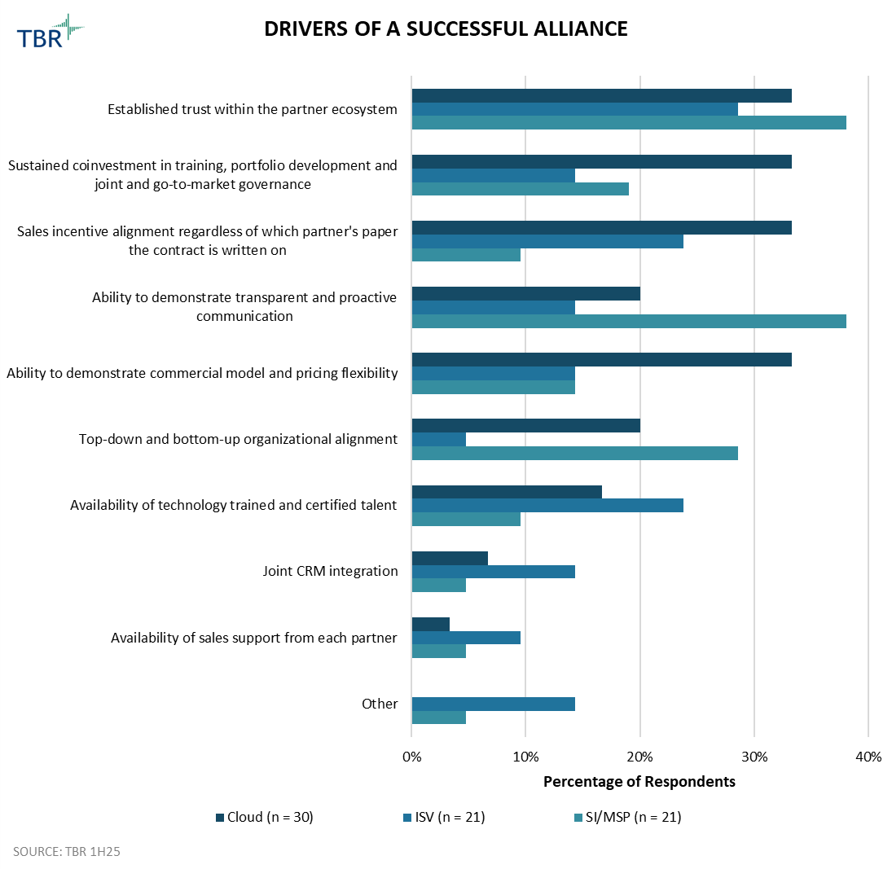
Drivers of a successful alliance
Across all vendors types, trust was deemed the most important attribute of a successful alliance. That said, compared to ISVs and systems integrators (SIs), cloud vendors value measurable drivers such as willingness to coinvest, alignment of sales incentives, and pricing model flexibility.
Services vendors are leading the charge with outcome-based pricing, though these vendors are far from delivering this model at scale. Although we expect some SaaS vendors will continue exploring outcome-based pricing, at least as part of a hybrid model, the infrastructure vendors are not equipped to implement a similar strategy, suggesting a potential challenge ecosystem participants will need to navigate.
Given their enterprise access, global systems integrators (GSIs) remain invaluable to hyperscalers, creating opportunities for SIs to expand in areas increasingly influenced by GenAI like managed services
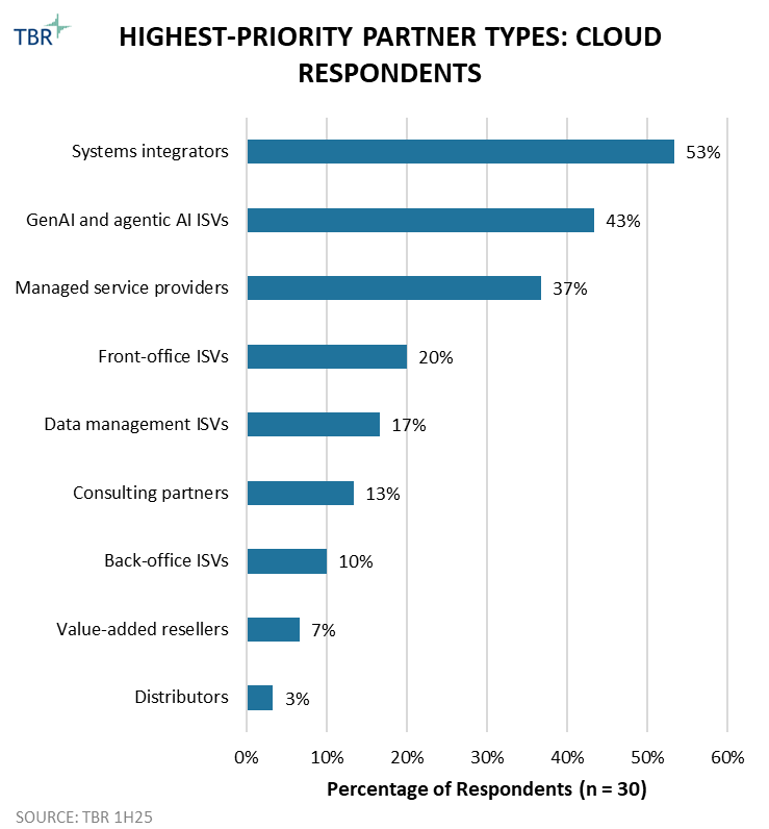
Priority partner types
Customers are increasingly realizing that to take advantage of AI, they need their infrastructure and applications modernized in the cloud. With the vast amount of enterprise data still residing on premises, there is a lot of opportunity ahead, and the cloud vendors recognize the influence SIs have with enterprises still carrying large amounts of tech debt. In fact, the big three hyperscalers are expecting partner attach rates above 80% for large deals, a strong recognition that the SIs are using the C-Suite to close deals, largely within the Fortune 1000.
Cloud providers are also paying more attention to managed services providers (MSPs). To be clear, this is not just niche MSPs but also existing SI partners that are expanding further into managed services. We believe these results are largely driven by GenAI, which is creating a need for services vendors to not only help customize an AI model but also maintain that model as part of an ongoing initiative. AWS has been making heavy investments here by increasing Market Development Funds (MDFs) for MSP partners and validating MSP Specialization partners on the AWS Marketplace landing page for professional services.
GenAI ISVs have become an emerging priority, and that is one of the big ways AI is changing alliances: There is simply a bigger field to choose from. Our survey also found that cloud vendors’ priorities over the next three years will focus less on re-tiering existing partners or rethinking investments and more on bringing new partners into their programs. We believe this speaks to all the new model providers and AI startups cloud vendors are trying to attract.
AI shifts alliances from an optional enhancement to a core requirement, forcing ISVs and partners to prove differentiated value beyond hype
Vendor perception
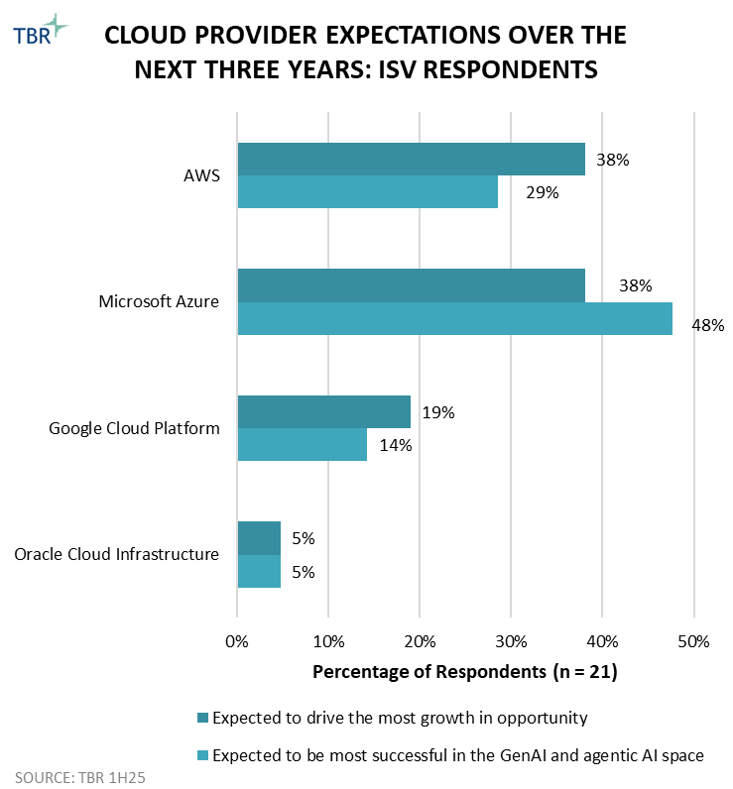
AI and GenAI are beginning to influence ISV partnerships, though most respondents still see themselves in the early innings. Nearly half of ISVs indicated GenAI has had no current impact on their alliance activity, underscoring the cautious pace of adoption. Where ISVs are engaging, the emphasis is largely on internal training programs and selective productivity use cases rather than external, cosell opportunities. ISVs are prioritizing workforce readiness and operational efficiency before extending GenAI into broader customer-facing partnerships. At the same time, expectations are shifting. A clear majority of respondents anticipate at least a moderate impact from GenAI on their alliances over the next three years, suggesting a steady transition from experimentation to applied use cases. Microsoft Azure was cited by nearly half of respondents as the cloud provider best positioned to capitalize, reflecting its Copilot-led attach strategy and strong marketplace presence.
Concerns remain pronounced, particularly around data security, IP ownership and regulatory alignment. These risks create friction in building joint solutions, as ISVs weigh the benefits of innovation against the potential liabilities of codeveloping with hyperscalers. Integration complexity adds another layer of hesitation, especially for smaller ISVs without extensive engineering resources. Overcoming these barriers will require trust frameworks that clarify accountability for data, intellectual property and compliance. For ISVs, the path forward lies in balancing internal GenAI experimentation with external signaling to partners, while building the governance models needed to scale alliances confidently. The result will be alliances that are both commercially viable and resilient to the risks that have so far hampered broader adoption.