Open RAN Adoption in 2024
The open RAN market is developing slowly due to technological complexity and relatively high cost compared to classic RAN. These factors mean the open RAN market is unlikely to scale to mainstream adoption in 2024.
Current Trend in Open RAN
Despite heavy (and sometimes excessive) marketing by vendors and hope among communication service providers (CSPs) around open RAN, the reality is that the technology remains immature.
Open RAN gear has been implemented successfully and is running live traffic in a few commercial networks (mostly in greenfield environments) in various parts of the world, but significant gaps still need to be closed in feature parity, performance parity and implementation cost parity with traditional RAN before open RAN can truly replace or augment traditional RAN.
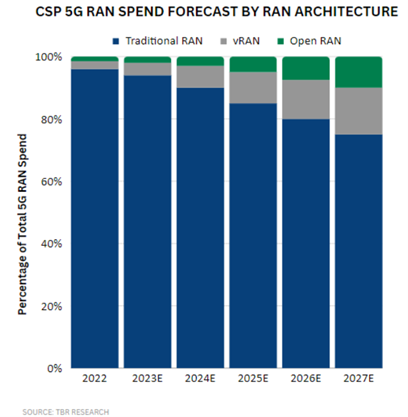
This inflection point remains at least another year away, and until this occurs, open RAN will likely remain a very small portion of the overall RAN market.
Watch 2024 Telecom Predictions session – 2024 Telecom Industry Outlook: Navigating Macroeconomic and Industry-specific Turbulence
Open RAN Outlook for 2024
CSPs that have been clamoring for open RAN remain committed to the technology, but there is increasing acceptance that open RAN is not ready to be commercially deployed at scale (especially not in areas of the macro layer that are heavily trafficked) as a viable alternative to traditional, purpose-built RAN — and may not be viewed as ready at least through 2024. As such, open RAN will continue to have a limited impact on the RAN market in 2024.
Conclusion
CSP urgency to stay competitive from a time-to-market perspective in some markets has prompted many CSPs to continue down the traditional RAN architecture path, at least for their initial 5G deployments because this architecture is proved, ready and currently able to be scaled faster than open RAN and/or vRAN.
Significant hurdles (e.g., feature parity, performance parity and implementation cost parity gaps relative to traditional RAN) still need to be overcome for open RAN to commercialize, mature and scale, especially within brownfield network environments. Thus far, open RAN deployments have been primarily limited to greenfield networks, such as DISH Network and Rakuten Mobile, where the technology is easier to roll out.
vRAN, on the other hand, has been commercialized and is gaining traction in the broader RAN market, with key CSPs like Verizon deploying the technology at scale. TBR estimates more than 60% of the open RAN and vRAN segment will be vRAN through the forecast period.
Ultimately, CSPs will rally around an open vRAN architecture because it promises a range of benefits, including agility and greater cost efficiencies compared to the traditional RAN architecture (open vRAN is theoretically able to provide cost savings in excess of 50% versus traditional RAN, representing a major incentive for CSPs that are trying to mitigate cost pressures amid the inexorable rise in data traffic on their networks).
To learn more about TBR’s predictions for the telecom market in 2024, download your free copy of Top Predictions for Telecom in 2024, featuring a look at the telecom industry response to macroeconomic and industry-specific challenges.




 Technology Business Research, Inc.
Technology Business Research, Inc.